Identity is a set of identity attributes which needs to be established in real world or digital world. Identity evidence links these attributes to the applicant. Where in the real word the identity is established using visual recognition, state’s trusted records, etc. In the digital world we rely on strong authentication and tokens which can be trusted by other internet users. This trust is established through various schemes, tasks and cryptographic operations.
Even though many more digital services are popping up every day, and with arrival of Covid-19 pandemic, world is looking towards ways to establish trusted identity on the internet. ETSI has defined Mobile Signature Service (MSS or more commonly Mobile ID/PKI) as “A Universal method using a Mobile device to confirm a Citizen’s intention to perform a Transaction.” These transactions prove their authenticity with digital certificates (or PKI certificates) with details about the owner and are issued by certificate authorities (CAs) or Trust Service providers (TSPs). Therefore, CAs/TSPs hold great importance and act as critical trust anchor of PKI / MobileID (mobile based strong digital identity) technologies. Hence, solving our many challenges related to our identity problems on the internet.
MobileID technology (IETF PKIX) makes use of asymmetric cryptography to create a binding between two distinct elements: asymmetric public key and user’s Distinguished MSISDN or Citizen SSI/IDNumber (or corresponding identity). The important elements of using PKI technology are:
- the mobile user’s private key is extremely well protected
- the binding represented by a certificate can be openly shared with applications
- applications must be able to trust the certificate issued by the CA.
This trust feature is called a Level of Assurance (LoA). LoA is achieved by creating a registration process which verifies the user’s identity and keys before it registers a certificate. When a user registers a certificate, the registration authority can request only certificates of a specific assurance level depending on the security needs. Ideally the citizen’s individual certificates needs to be of LoA 3 or higher. Kiuru MSSP 6.0, offers support for multiple levels of assurance, starting from Click-OK LoA2 authentication, to strong eIDAS compliant LoA4 authentication.
Certificates should only be issued by the CA if the user information have been verified (by RA) and principles of KYC are upheld. These certificates must to be validated before each transaction. Ideal CA/TSP platforms includes certificate management tools for SSL/TLS communication, XML Signatures, certificate validation tools, auditing/monitoring tools as well as SOAP/REST communication stacks and message handlers.
User Enrollment / Registration
To onboard a new user to their service, CAs need to often have capabilities of registering agent (RA) themselves, outsource it to a RA entity or utilize a dedicated and user-friendly software platform like Kiuru MSSP 6.0 for CA/TSPs to implement and deliver managed digital signature services to application providers.
RA acts as an integral part of MobileID / PKI technology, as onboarding a new verified new user needs to take into consideration principle of identity proofing. Identity proofing is the process of proving with the required degree of reliability that the applicant’s claimed identity is correct, then RA can request for certificate registration.
Registration Authority (RA) is an actor defined in multiple standards covering identity. For example in ETSI TS 119 461 context the RA term can be defined as ‘RA is either a Registration officer or a Registration Application – automatic system acting on behalf of the CA/TSP which provides registration process execution.’
A classical way to do the mobile registration in Mobile ID / PKI projects, before issuing user certificates is to collect and validate end-user identity attributes, verify that the security token is in possession of the user, generate on-board a key pair and user defines a PIN, and request for a certificate for 3 to 5 years with said identity attributes.
User enrollment / registration via Kiuru MSSP
Steps below list the user registration and certificates issuance process:
- Initial authentication of the user by RA
- Verification of user identity details by the RA agent. RA verifies identity of the user and subscription details through 3rd part services and subscription details.
- Starting activation process based on the user’s selected wPKI profile.The activation process will generate the KeyPair i.e private and public keys for the user.
- If wPKI client is a SIM/eSIM, after KeyPair generation, user is asked to define PIN to protect private keys.
- If wPKI client is an APP, after KeyPair generation, user is asked to define PIN to protect private keys
- MSSP sends the Public key and user’s identity attributes to the CA in a certificate signing request (CSR).
- Storing received certificates to MSSP’s database of user certificates.
- MSSP fetch the certificate from the database when needed.
- Users can sign/authenticate themselves from their respective wPKI clients.
The figure below depicts the design for complete Mobile ID / PKI project, how the certificates are registered, how they are obtained when needed and pin point operations for user enrollment and certificate issuance.
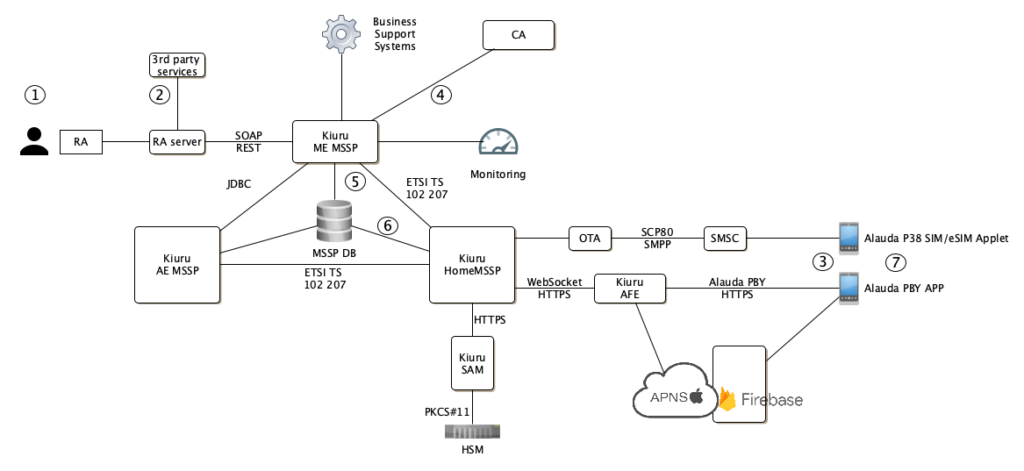
Kiuru Management Entity (ME) MSSP integrates with Registration Authorities who provide MSS registration services to end-users or corporate services. Kiuru ME MSSP provides secure service management functionality (MReg and SPML2 interfaces for service and account management and CA interface for certificate management) for Mobile ID / PKI projects.
After the registration user may start their Mobile ID usage. The usage can continue until the certificate is revoked or the certificate expires. In classical model the user must run the registration process again from start.
Feel free to get in touch with us if you want a user-friendly software for your TSP, implement Identity proofing principles in your user onboarding process, implement authentication/sign in service, document Signature solution, or want to increase your user adoption of PKI services.
Publish Date: 3 March 2022
Written and Edited by: Ammar Bukhari & Eemeli Miettinen
References
1. ETSI TS 119461: Policy and security requirements for trust service components providing identity proofing of trust service subjects: https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_ts/119400_119499/119461/01.01.01_60/ts_119461v010101p.pdf
2. Kiuru MSSP: https://www.methics.fi/methics-product-portfolio/kiuru-mssp/
3. Certificate Authority: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Certificate_authority
4. Strong Identification: https://www.methics.fi/strong-electronic-identification-scenarios-for-the-future/
5. PKI certificates: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_key_certificate
Image by Gerd Altmann from Pixabay
