In many cases, the law of land falls behind technological advancements. However, it’s not the case with the world of PKI, authentication and digital signatures. First adopted legislation for digital signatures was adopted by the European Union in the previous century, almost 3 years before Methics was founded. When the legislation for digital signatures were drafted, one of the main condition was to allow usage of a secure signature creation device. At that time, ID cards with a unique identifier chip was the only go-to solution. Due to a dependency on extra hardware such as card reader etc., these solutions were present for some time, but had a slow adoption rate.
As the masses and organizations familiarized themselves with the age of internet, this situation changed with an advent in technology. As it is now possible to reuse existing two factor (2FA) and multi-factor (MFA) authentication without the use of additional hardware or software. Today’s smartphones and tablets can easily be exploited to encompass all the required features of Public Key Infrastructure for signature creation. Additionally, a cloud based signature server can support the cryptographic functions for strong customer authentication.
The European Commission has recognized this trend and with success of many national PKI and authentication projects across the world in public sector and enterprises. There has been significant development to make authentication services easier to use, set standards for software/hardware vendors, to follow and provide a wider range of services to the end-users upon their authentication.
Remote Signing is a new concept introduced after eIDAS regulation no. 910/2014 which enables the creation of QES – Qualified Electronic Signatures and AdES – Advanced Electronic Signature, using electronic signature creation device which followed the set standards. QES and AdES are managed remotely by a trust service provider (TSP) operating on behalf of the signer (user). The user’s signing key is securely held under the user’s sole control, and signature operations are done in a hardware security module (HSM) on the server end. These signatures carry the same legal weight as a written signature (in many world regions as well as EU-region) and may even be considered more secure as they provide a higher Level of Assurance. Image below depicts how eIDAS defines the environment of Remote Signing to maintain a higher level of assurance.
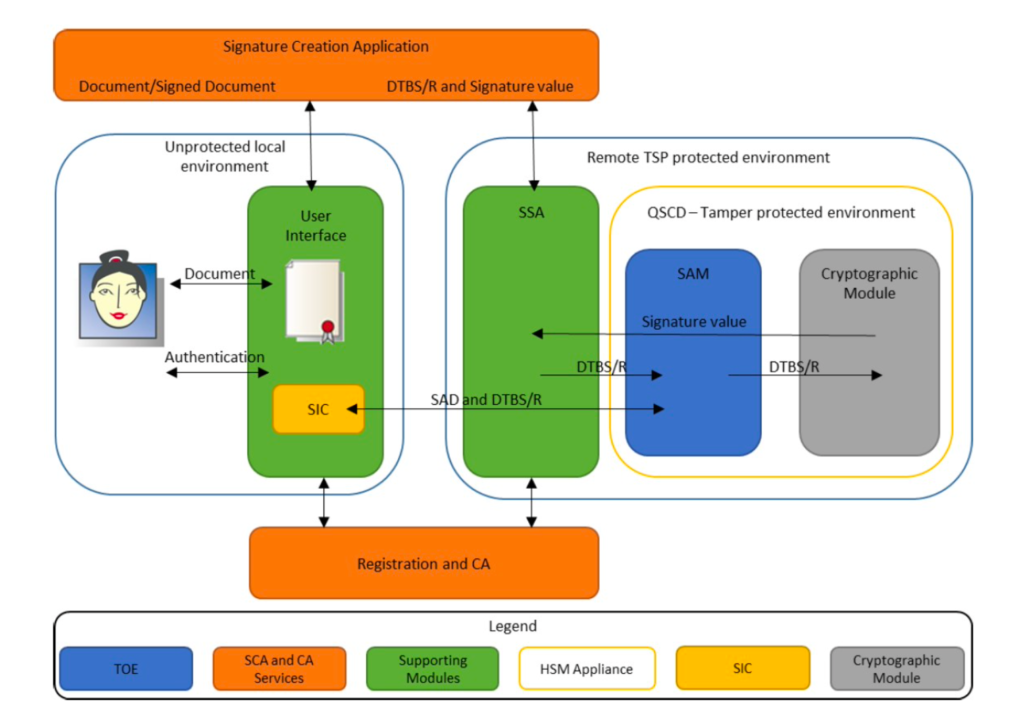
TSPs play a pivotal role in maintaining the trust in digital transactions for identities. They are required to apply use of specific management and administrative security procedures in order to guarantee that the electronic signature creation environment is reliable and used under the sole control of the signatory. This regulation also requires, for QES, the use of qualified electronic signature creation devices (QSCD) which utilizes specific software and hardware that ensures user’s signing (private) keys are under their complete control.
By using Remote Signing service, a user can create different type of digital signatures such as QES and AdES. A QES is an AdES with a qualified digital certificate that has been signed by a secure/qualified signature creation device, encrypted and processed. Signatures of QES and AdES kind have requirements of a secure and auditable environment to authenticate and store the signature creation data. To be considered at a qualified level, the electronic signature which is called QES must meet three requirements:
- Signature must be uniquely identified and linked to the signer/signatory through a digitally trusted certificate.
- Signature creation data (especially the private key) must be under the sole control of signer/signatory only. This signature creation data is used to the digital signature.
- Tamper-proof protections must be in place to identify if tampering has taken place with the data that accompanies the signature since the signing of the message.
To conclude the differences between QES and AdES, it can be said that QES enhances the security requirements and legal assurance that AdES provides through Remote Signing. However, creating a qualified signature from a qualified signature creation device and attaching a qualified digital certificate means only very few companies in the world which have trustworthy system supporting server signing (TW4S) to offer QES as a service. The TW4S, often called as Signature Activation Module (SAM) in eIDAS regulations, uses a Cryptographic Module to generate the signing key and create the digital signature value.
The implementation of both QES and AdES requires the implementation to be undisputed, non-repudiation and tamper-proof. Therefore, in order to perform Remote Signing (which signs with QES or AdES on behalf of the actual person) over the internet, eIDAS has defined two standards, EN 419 241-1: TW4S General System Security Requirements and EN 419 241-2: TW4S Protection Profile for QSCD for Server Signing, for organizations involved in implementing Remote Signing service.
By using these new standards, governmental, legal processes and local/international businesses, can be completed entirely over the internet. These standards greatly reduce risks of fraud, the need for in-person meetings, and finally can be be revolutionary for our digital transformation of public and private sector.
In order to competently design, develop, manage and maintain the TW4S services, companies involved in Identity business need to develop products on evolving technology and standards. Methics has been involved in providing built-on standards product, with high grade cryptography to securely authenticate mobile users.
Methics as a company pride ourselves in maintaining a mature modular platform, which is built on standards without having any vendor-locking and having broad technical capabilities for TSPs, Qualified TSPs, CAs, MNOs and Governments. With deployments across EMEA and APAC regions, Methics is serving authentication services to over 10 Million users. Additionally, our customer deployments have been certified according to various international standards such as:
- Common Criteria Standards EAL 4+ by EN 419 241-1
- Common Criteria Standards EAL 4+ by EN 419 241-2
- ETSI TS 102 203
- ETSI TS 102 204
- ETSI TS 102 206
- ISO 15408
Methics is the only solution provider in the world which provides multiple wireless PKI clients integrated into a single product. The product is able to perform QES and AdES on behalf of user by employing Methics Remote Signing Solution. Usual solutions in the market which implement Remote Signing for public sector and private sectors, provide one wireless PKI client i.e Smartphone App to implement the Remote Signing compliant to eIDAS-regulations. However, Methics provides wPKI clients for Remote Signing through:
- Alauda PBY Smartphone APP (SDK)
- Alauda B17 (non-PKI) SIM card applet
- Alauda mssCSP for desktop clients by authenticating through APP or SIM.
Using these three wPKI clients, implementer(s) of Remote Signing solutions can enhance the adoption of the solution by providing more options Image below depicts the complete solution overview of Methics Remote Signing Solution.
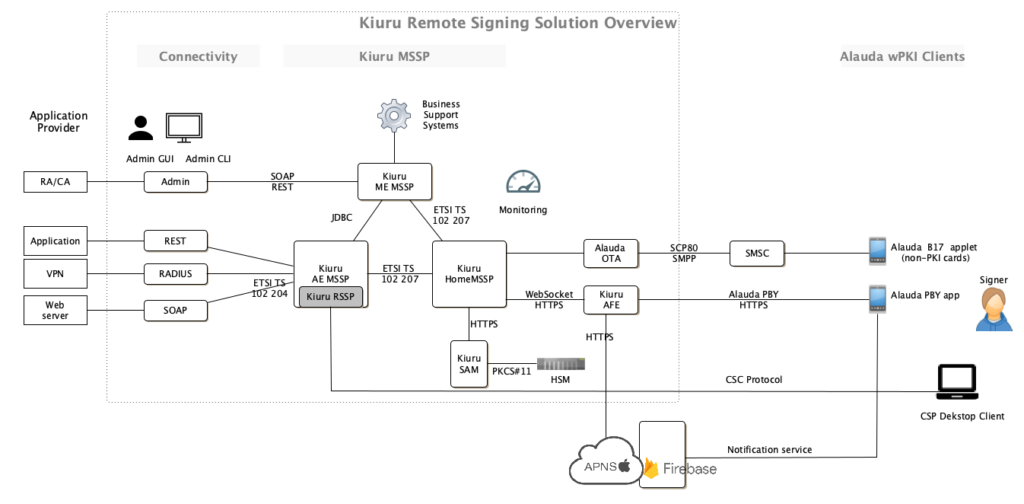
Methics’s complete product offering includes both SIM, Smartphone App, and desktop application based client, and necessary backend servers like MSSP & OTA. Using these mature products, Methics is able to offer solutions such as:
- Remote Signing with wPKI clients such as Smartphone App (Alauda PBY), desktop application client, and non-PKI cards with Alauda B17 Applet.
- Local Signing with wPKI clients such as SIM card with PKI components having Alauda P38 applet
- Kiuru Document Signing Service and Archiving
- Identity Proofing Portal
Methics has a long experience of working with PKI technology for implementation the MobileID / DigitalID. We have working with leading SIM card vendors, HSMs providers, and Certificate Authorities to a secure, and user-friendly software platform and products to implement and deliver managed digital signature services to application providers.
Feel free to get in touch with us if you want a user-friendly software for your TSP, implement authentication/sign in service, document signing solution, or want to increase your user adoption of PKI services.
Publish Date: 8 November 2021
Written and Edited by: Ammar Bukhari & Jarmo Miettinen
